Massimo Valentino1, Carmela Bonavolontà1, Antonio Vettoliere1, Ivo Rendina1, Berardo Ruggiero1, Paolo Silvestrini2,1
1 CNR- ISASI, Institute of Applied Sciences and Intelligent Systems, via Campi Flegrei 34, 80078, Pozzuoli (Naples), Italy
2 DMF – Dept. Of Mathematics and Physics Università della Campania “L. Vanvitelli” 81100 Caserta, Italy
Photodetectors are of great interest in various technological applications thanks to their ability to convert an optical signal into an electrical signal through light-matter interaction. Broadband photodetectors are used in multiple applications such as environmental monitoring, fire detection and astronomical observations. The optical and electronic characteristics of the photosensors studied at ISASI are useful in different applications and sensitive in a range of light spectrum starting from UV up to infrared. In this research activity, a heterojunction photodetector based on reduced graphene oxide (rGO) was created using the spin coating technique. Preliminary analysis of the electro-optical properties of thin films of GO and rGO was carried out depositing the films on a glass substrate. The analysis of the transmittance in the UV-Vis-IR range of the GO and rGO thin films revealed a wide absorption range, while through the absorbance analysis the gap in the absorption energy band of the rGO has been estimated to be approximately 2.8 eV. The effect of the GO reduction process on the photoresponse capability of the device based on the rGO/n-Si heterojunction was studied by performing measurements of the current-voltage characteristics (Fig. 1 (a)) using laser diodes with wavelengths in the UV – IR spectral range. Furthermore, the current-voltage characteristics were interpreted by proposing an energy band diagram of the rGO/n-Si heterojunction. The realized photodetector demonstrates a photoresponse in a wide spectral range with a responsivity and detectivity of 0.20 A/W (Fig. 1 (b)) and 7 × 10^10 cm Hz/W, respectively. The results of this research activity have demonstrated the feasibility of creating a device based on rGO/n-Si heterojunction to detect from UV to IR light, with good performance so that it can be included among the next generation of broadband photodetectors useful for innovative applications compatible with silicon device technology.
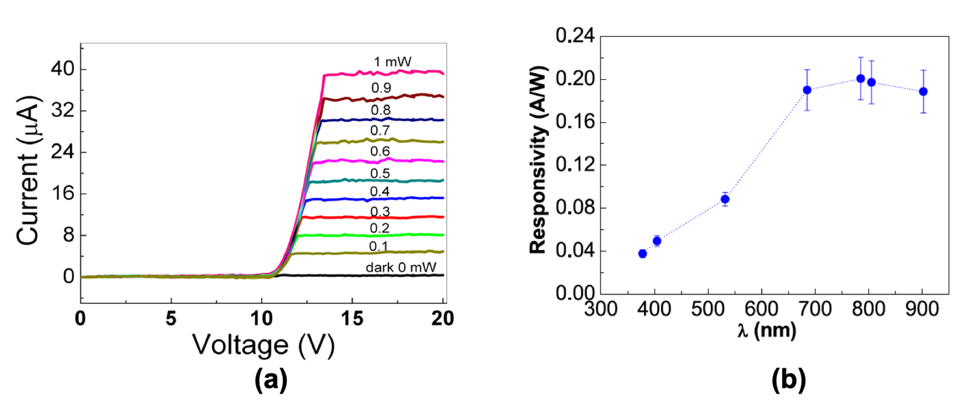
Figure 1: a) Current-voltage characteristic of the photodetector based on rGO/n-Si heterojunction using a laser diode at a wavelength of 378 nm at various powers (from 0.1 mW to 1 mW); (b) Responsivity of the device based on rGO/n-Si heterojunction in the UV-Vis-IR spectral range.